The Problem
Real-time linking of transactions, accounts, wallets, and blocks within and across blockchains is not possible with current solutions. Instead, the user must either rely on batch processing, which means results are out of date, or perform recursive lookups across table joins, which means unacceptable latency.
The Solution
Graph data structures are ideal for modeling the relationships described in blockchain events. Flows of cryptocurrency between accounts and wallets are ideal inputs for graph data modeling. Accounts, addresses, time references, devices, assets, transaction details, etc. are all examples of categorical data connected by relationships and are therefore ideal to be represented as the nodes, edges, and properties provided in a graph data model. Most importantly, relationships between entities are first class citizens in the data model so the costs and complexity associated with table joins is entirely eliminated.
Quine easily ingests event feeds from multiple sources and creates a single unified view of activity on the blockchain(s). When fraudulent activity is reported, or when evidence of fraud emerges, Quine’s standing queries instantly recognizes the patterns and triggers an alert. Now the client is not only detecting the fraudulent behavior in real time but blocking transactions before they can complete. Of course, many fraud alerts are delivered well after a transaction occurs and the Quine streaming graph can instantly provide a complete list of past transactions for a wallet or block to aid investigations or to block future transactions with related parties.

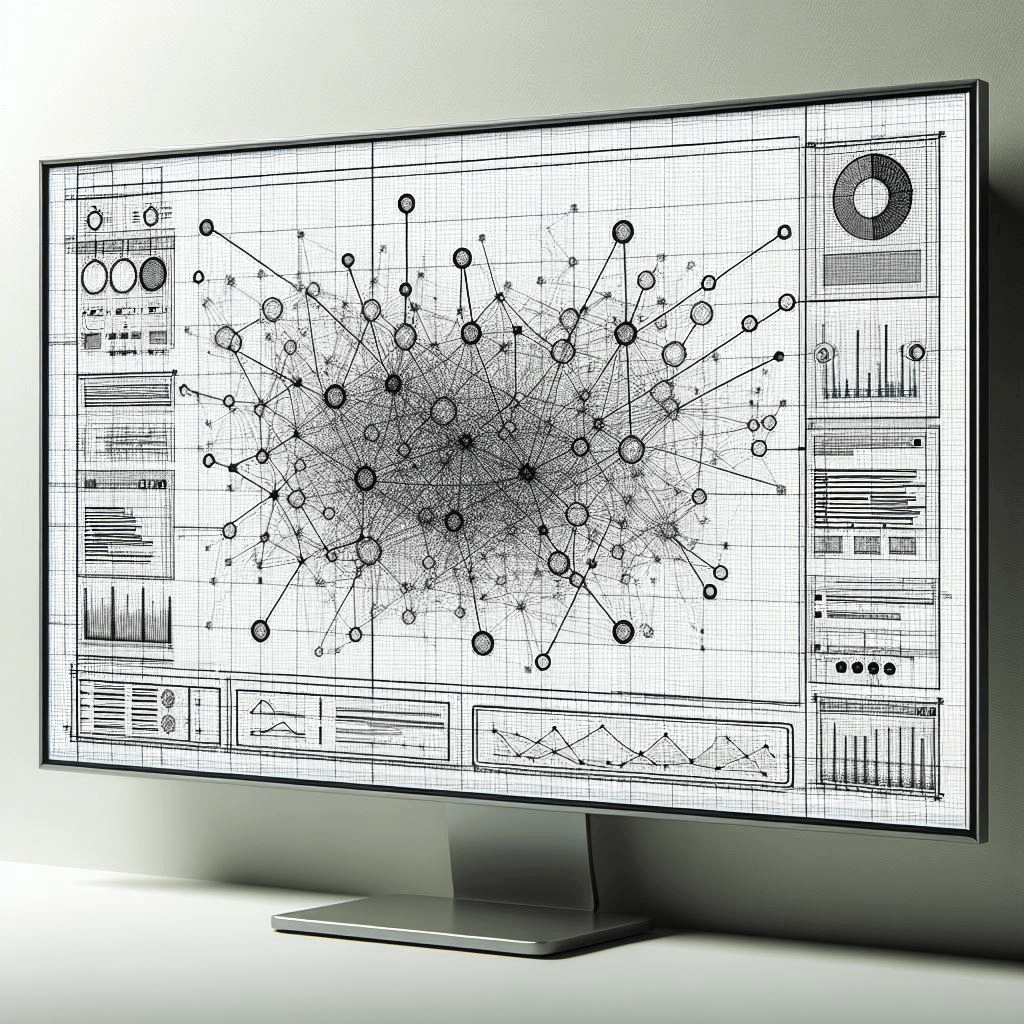
Graph is the ideal data model for blockchain relationship tracing.
In the above screenshot from Quine’s Exploration UI, you can see how Quine makes it easy to trace all the accounts with which an account engaged in fraudulent activities interacts.
Watch thatDot’s founder, Ryan Wright, demonstrate using Quine to tag fraudulent accounts and track transactions:
Key Value Take Away
- Sub 5ms Access to Complete trace history
- Adapt to new blockchains rapidly with streaming ETL built in
- Real-time materialization of wallet, block and transaction state
- On premise software to deploy in your data center or cloud of choice
- Integrates with existing Apache Kafka, AWS Kinesis, data lake, and API event sources